

(d) Mg(NH 4)PO 4, magnesium ammonium phosphate, an essentially insoluble substance used in tests for magnesium (c) Mg(OH) 2, magnesium hydroxide, the active ingredient in Milk of Magnesia (b) CaCO 3, calcium carbonate, the active ingredient in many over-the-counter chewable antacids (a) AgI, silver iodide, a solid with antiseptic properties Write the dissolution equation and the solubility product expression for each of the following slightly soluble ionic compounds: Writing Equations and Solubility Products For example, a saturated solution of silver chloride is one in which the equilibrium shown below has been established. A solute with finite solubility can yield a saturated solution when it is added to a solvent in an amount exceeding its solubility, resulting in a heterogeneous mixture of the saturated solution and the excess, undissolved solute.
Recall from the chapter on solutions that the solubility of a substance can vary from essentially zero ( insoluble or sparingly soluble) to infinity ( miscible). This section applies previously introduced equilibrium concepts and tools to systems involving dissolution and precipitation. An understanding of the factors affecting compound solubility is, therefore, essential to the effective management of these processes. These equilibria underlie many natural and technological processes, ranging from tooth decay to water purification. Solubility equilibria are established when the dissolution and precipitation of a solute species occur at equal rates.

To decide solubility, we have to look solubility product or solubility data from books or any other resource. Some metal hydroxides are soluble and some are not. Magnesium hyroxide is not soluble in heptane or alcohols. Would magnesium hydroxide be soluble in heptane? See one white precipitate will dissolve when adding aqueous NaOH. But, magnesium hydroxide is not a amphoteric hydroxide. Therefore it dissolve in aqueous NaOH and form sodium zincate

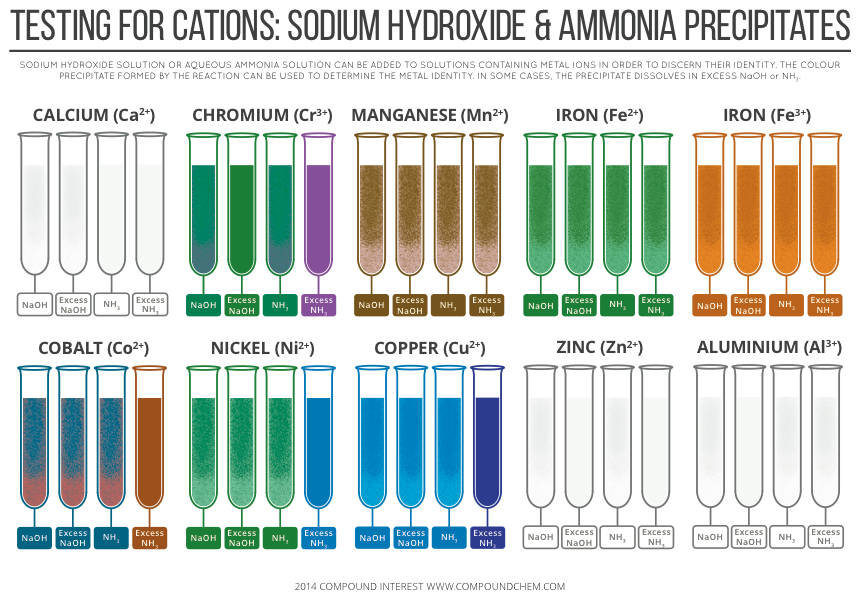
How do you identify magnesium hydroxide and zinc hydroxideīoth magnesium hydroxide and zinc hydroxide are insoluble in water and form white precipitates. Therefore Mg(OH) 2 cannot be an amphoteric metal hydroxide. Magnesium hydroxide is not soluble when aqueous NaOH is added. Is Mg(OH) 2 an amphoteric metal hydroxide list This is the summary of solubility of all metal hydroxides. List of metal hydroxides solubility with colours Metal hydroxide Solubility Colour of solid state Colour of in the water LiOH soluble white colourless solution NaOH soluble white colourless solution KOH soluble white colourless solution Be(OH) 2 insoluble white a white precipitate with colourless solution Mg(OH) 2 insoluble white a white precipitate with colourless solution Ca(OH) 2 insoluble in higher concentrations of ions white a white precipitate in higher concentrations or colourless solution Al(OH) 3 insoluble white a white precipitate in higher concentrations or colourless solution Sr(OH) 2 soluble white colourless solution Ba(OH) 2 soluble white colourless solution Cr(OH) 3 insoluble green form a green precipitate with green colour solution Mn(OH) 2 insoluble white/pink form a white or pink precipitate Fe(OH) 2 insoluble green form a green precipitate with green colour solution Fe(OH) 3 insoluble brown form a brown precipitate with brown colour solution Co(OH) 2 insoluble light blue form a blue precipitate with blue colour solution Ni(OH) 2 insoluble green form a green precipitate with green colour solution Co(OH) 2 insoluble light blue form a blue precipitate with blue colour solution Cu(OH) 2 insoluble blue form a blue precipitate with blue colour solution Zn(OH) 2 insoluble white form a white precipitate with colourless solution Pb(OH) 2 insoluble white form a white precipitate with colourless solution


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
